Natural Science Unit 4. The Plant Kingdom
Hello everybody!
Here it is the main information of Unit 4. Plant Kingdom. Good luck!
1. CLASSIFICATION OF PLANTS:
The Plant Kingdom includes more than 250 000 species. All these plants can be classified into two main groups: flowering and non-flowering plants.
FLOWERING PLANTS
Flowering plants are the biggest group of plants on Earth. Most flowering plants use sexual reproduction (they grow flowers which are their reproductive organs). These plants reproduce through seeds and produce them in two different ways:
- Angiosperms: pollinated flowers produce fruits with seeds inside. Examples: roses, cherry trees, blackberries, rice ...

- Gymnosperms: have small flowers. They don’t produce any fruit and their seeds develop in cones. Many gymnosperms, such as pine trees, have long thin leaves called needles.

NON- FLOWERING PLANTS
Non-flowering plants do not produce seeds. They reproduce asexually using spores.
There are two main groups:
- Ferns: Ferns are one of the oldest plants on Earth. They evolved more than 300 million years ago.
2. PARTS OF THE PLANT:
Most plants have three main parts: roots, stem and leaves.
- ROOTS:
1. The roots hold the plant to the ground.
2. They absorb water and minerals needed for nutrition from the ground through the root hairs.
- STEM:
1, The stem holds up the other parts of the plant.
2. It transports water and minerals to the leaves for photosynthesis. The food produced through photosynthesis then travels to the other parts of the plant.
- LEAVES:
1. Leaves contain chlorophyll, a green substance which is necessary for photosynthesis.
2. Most leaves have two mains parts: the petiole and the blade.
3. PLANT NUTRITION AND RESPIRATION:
- NUTRITION:
All living things need energy to perform their basic functions. So, plants produce their own food through the process of photosyntesis.
1. The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
2. Xylem cells transport this mixture of water and minerals, called raw sap, through the stem to the leaves.
3. Leaves absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) through their stomata. In certain parts of plant cells called chloroplasts, chlorophyll collects solar energy to transform water, minerals and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen (O2).
4. Phloem cells carry the glucose, the plants’ food, through the stem to all the parts of the plant.

Here it is the main information of Unit 4. Plant Kingdom. Good luck!
1. CLASSIFICATION OF PLANTS:
The Plant Kingdom includes more than 250 000 species. All these plants can be classified into two main groups: flowering and non-flowering plants.
Flowering plants are the biggest group of plants on Earth. Most flowering plants use sexual reproduction (they grow flowers which are their reproductive organs). These plants reproduce through seeds and produce them in two different ways:
- Angiosperms: pollinated flowers produce fruits with seeds inside. Examples: roses, cherry trees, blackberries, rice ...

- Gymnosperms: have small flowers. They don’t produce any fruit and their seeds develop in cones. Many gymnosperms, such as pine trees, have long thin leaves called needles.

NON- FLOWERING PLANTS
Non-flowering plants do not produce seeds. They reproduce asexually using spores.
There are two main groups:
- Ferns: Ferns are one of the oldest plants on Earth. They evolved more than 300 million years ago.
- They have roots and strong stems which grow under the ground.
- They have large leaves called fronds and they produce spores inside sori on the underside of the fronds.
- They have very simple stems and leaves.
- Their roots are called rhizoids.
- And they produce spores inside capsules.
2. PARTS OF THE PLANT:
Most plants have three main parts: roots, stem and leaves.
- ROOTS:
1. The roots hold the plant to the ground.
2. They absorb water and minerals needed for nutrition from the ground through the root hairs.
- STEM:
1, The stem holds up the other parts of the plant.
2. It transports water and minerals to the leaves for photosynthesis. The food produced through photosynthesis then travels to the other parts of the plant.
- LEAVES:
1. Leaves contain chlorophyll, a green substance which is necessary for photosynthesis.
2. Most leaves have two mains parts: the petiole and the blade.
- Veins in the blade support the leaf and carry water and minerals.
3. PLANT NUTRITION AND RESPIRATION:
- NUTRITION:
All living things need energy to perform their basic functions. So, plants produce their own food through the process of photosyntesis.
1. The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
2. Xylem cells transport this mixture of water and minerals, called raw sap, through the stem to the leaves.
3. Leaves absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) through their stomata. In certain parts of plant cells called chloroplasts, chlorophyll collects solar energy to transform water, minerals and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen (O2).
4. Phloem cells carry the glucose, the plants’ food, through the stem to all the parts of the plant.

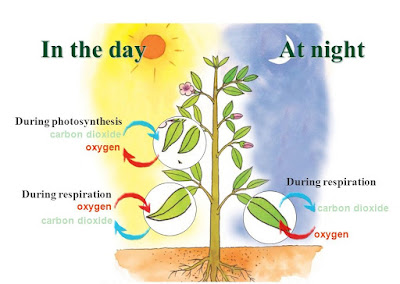
- RESPIRATION:
Plants don’t just
consume oxygen, they produce it too. This happens during the day as
part of photosynthesis, when plants produce more oxygen than they need.
At night, when photosynthesis stops, plants release carbon dioxide.
At night, when photosynthesis stops, plants release carbon dioxide.
- IMPORTANCE OF PHOTOSYNTESIS:
1. It provides us with oxygen to breathe.
2. It consumes carbon dioxide, which is toxic to most living things.
3. It transforms water and minerals into food.